Medium Voltage (MV) switchgear is an indispensable switching device in industrial and commercial electrical systems, serving the purpose of protecting the system and personnel. So, what is MV switchgear, what is its structure, function, and how is it classified? We have compiled detailed information in the article below.
What is Medium Voltage Switchgear?
Medium Voltage Switchgear is a dedicated switching device for medium voltage, which functions to distribute electrical energy and to interrupt voltage to protect the system against overload and short circuit faults.
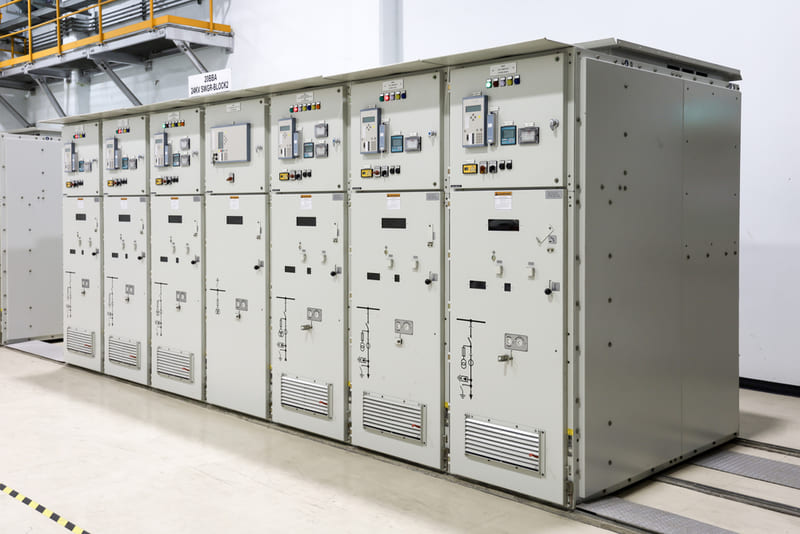

According to IEC 62271-200 standard, this equipment is designed, manufactured, and tested for switching, protection, and control purposes in alternating current (AC) systems from 1kV to 52kV. Therefore, it is applied in secondary distribution networks such as secondary substations, light industry, or wind power generation plants. Additionally, MV switchgear is also used for hotels, shopping centers, and high-rise buildings.
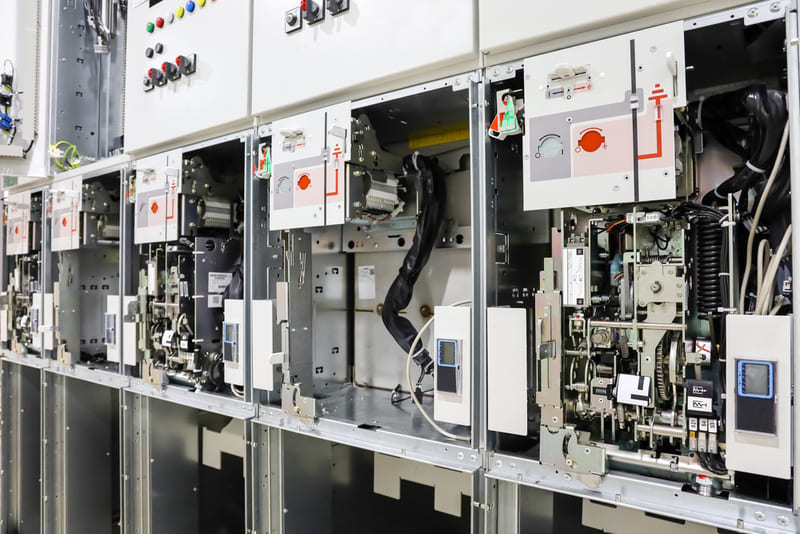
MV switchgear has the following specific characteristics:
- Large operating voltage source: from 1kV to 52kV according to IEC 62271-200 standard.
- Continuous discharge current: from 600A to 4000A.
- Operates based on protective relays to detect any dangerous abnormalities in the electrical circuit.
- Appears in many substations, or combined with other equipment such as: minimum oil circuit breakers, bulk oil circuit breakers, SF6 gas insulation, etc.
- Can be installed indoors or outdoors, even in harsh environments such as: vacuum, oil, insulation medium, etc.
- High longevity, easy operation, and causes no noise when interrupting the current,
Structure of Medium Voltage Switchgear
Current MV switchgear is designed in the form of MV electrical panels/enclosures, consisting of main components such as the enclosure, insulating material, circuit interrupting devices, and smart switching devices.

Enclosure
This is the protective layer for the MV switchgear, usually made of steel sheet, about 2mm, and coated with electrical insulation, making it very safe and robust.
Insulating Material
The insulating medium is the environment inside the MV switchgear enclosure that protects live components like busbars, bushings, etc., from arc faults. Some insulating materials used for MV switchgear include:
- Air: The most common and cheapest insulating medium, but it has the weakest dielectric properties, making live components inside susceptible to electric arcs.
- Gas: The gas typically used as an insulating medium for MV switchgear is Sulfur Hexafluoride (SF6). The electrical contacts are sealed inside a tank containing compressed SF6 gas.
- Solid Dielectric in Air Technology: A combination of non-conductive materials with low-humidity air gaps, providing low dielectric loss, high mechanical strength, and resistance to thermal and chemical degradation.
- Liquid: Typically insulating oil that is flame-resistant, including three common types: mineral oil (petroleum-based); E200 fluid which is low-viscosity, non-toxic, polyol ester-based, flame-resistant, with good dielectric, thermal, and physical properties; FR3 fluid formulated from vegetable oil and enhancing additives.
Circuit Interrupting Devices
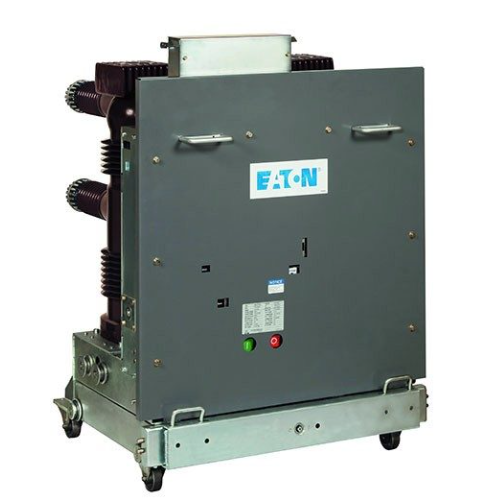

This component includes main circuit interrupting devices (fuses, circuit breakers) and switches, typically such as:
- Air Switches: Switching devices that use air as the dielectric medium, usually having a lower interrupting capacity than oil or vacuum switches but being more economical.
- Fuses: Devices that interrupt overcurrent by melting at a specified time/temperature. In MV switchgear, fuses are combined with switches to increase the capability of circuit closing/opening and overload protection.
- Oil Switches: Switching devices submerged in an oil-filled enclosure. These devices typically appear in pad-mounted MV switchgear.
- Vacuum Circuit Breakers (VCB): A type of circuit breaker where the arc extinguishing process takes place inside a sealed vacuum chamber. VCBs can interrupt much higher overvoltage faults than air circuit breakers.
- Vacuum Fault Interrupters (VFI): Functions as an overcurrent protection device, capable of replacing fuses and switches.
- Vacuum Switches: A type of electrical switch capable of interrupting current inside sealed vacuum chambers. Vacuum switches require less space than air or oil switches and can be used at higher voltages.
Metering Equipment
This equipment measures three main values:
- Asymmetrical Interrupting Current: The largest fault current that the circuit breaker and fuses can safely interrupt, measured in symmetrical Amps RMS. For example, medium voltage VCBs have an interrupting current of about 25 kAIC to 63 kAIC.
- Short Circuit Rating (SCR): An index evaluating the MV switchgear's capability to interrupt the circuit and withstand the short-circuit current during a fault.
- Continuous Current Rating: The current value that the main circuit breaker and main busbar inside the MV switchgear can continuously carry without damaging the equipment. MV switchgear typically has a continuous current rating from 600A to 4000A.
- Maximum Rated Voltage: The voltage value at which the MV switchgear can operate. For example, a 15kV MV switchgear can be applied at various actual voltages including: 12.47kV, 13.2kV, 13.8kV, and 14.4kV.
Smart Switching Devices
The integration of Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs) such as smart circuit breakers, sensors, and microprocessor-based meters helps enhance the performance of MV switchgear. Additionally, when MV switchgear is networked, it allows operators to apply cloud computing solutions for detailed data analysis of the power distribution system.
Classification of Medium Voltage Switchgear
MV switchgear is classified according to various criteria.
According to IEC 62271-200 Standard
- Insulating Material: Switchgear using gas, air, and liquid insulation materials, etc.
- Partitioning Material between Compartments: PM (Partially Metal-enclosed) / PI (Partitioned)
- Internal Arc Fault (IAC classification): AFL (Accessible from Front and Lateral) / AFLR (Accessible from Front, Lateral, and Rear)
- Continuity of Service: LSC-1 / LSC 2-A / LSC 2-B
According to Function
- VCB (Vacuum Circuit Breakers): Vacuum switching devices with a large short-circuit interrupting current, ranging from 15kA to 50kA or large currents from 100A to 4000A.

- VCS (Vacuum Contactor Switches): A type of vacuum contactor with a very large switching capability. The number of switching operations for VCS can be up to 2,500,000 times. This type is widely used in conveyor systems, elevators, pumping stations, substations, etc.
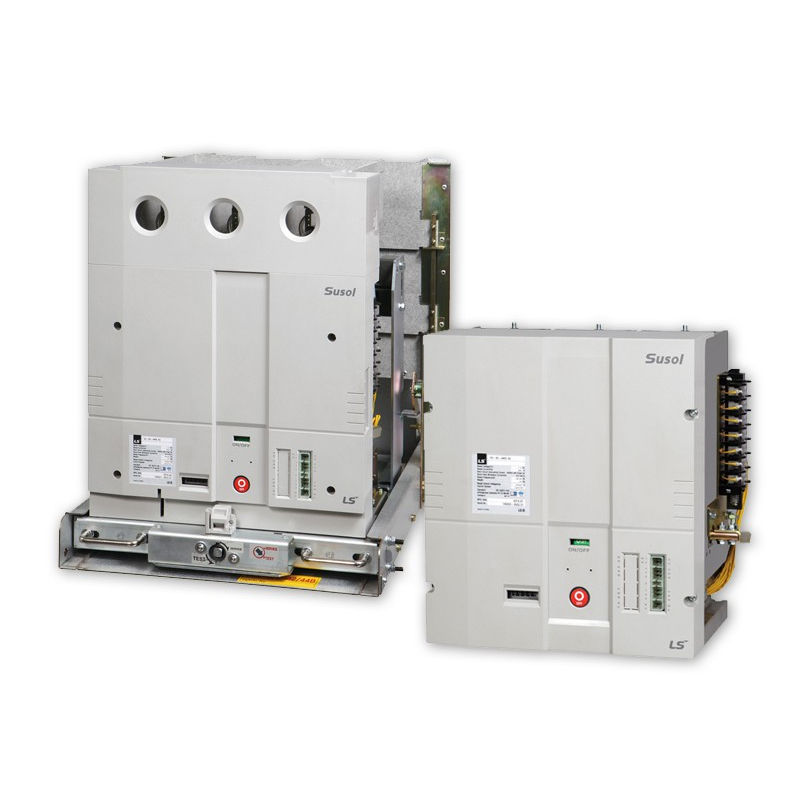

- VTS (Vacuum Transfer Switches): Vacuum switching devices used to switch power between grid-to-grid sources or grid-to-generator sources. VTS has a rated current from 400A to 600A. The common short-circuit interrupting current is 12.5kA and the control voltage is 100V/110VDC.

- Recloser: A circuit breaker that automatically recloses when a fault occurs for only a short period to ensure power continuity on the system. Current reclosers are mainly three-phase, with added lightning arresters.
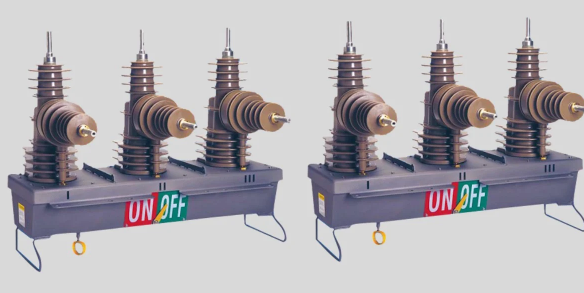
- LBS (Load Break Switches): Load break switches with a function similar to a sectionalizing switch. LBS not only switches but also has the capability to protect the electrical system.
According to Structure
- Compact MV Switchgear: Designed as three phases in a single tank or in an isolated phase configuration, suitable for installation in small, confined spaces. This type is designed, manufactured, and tested according to IEEE C37.20.9 and IEC 62271 performance standards.
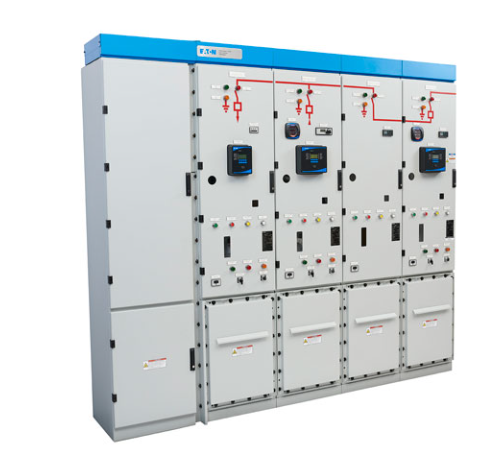

- Metal-Clad MV Switchgear: All live components such as busbars, metering equipment, main circuit breakers, and switches are enclosed in separate metal compartments. The rated voltage level for this type of switchgear is approximately 5kV to 38kV and it is applied in factories, power generation, and transmission facilities.
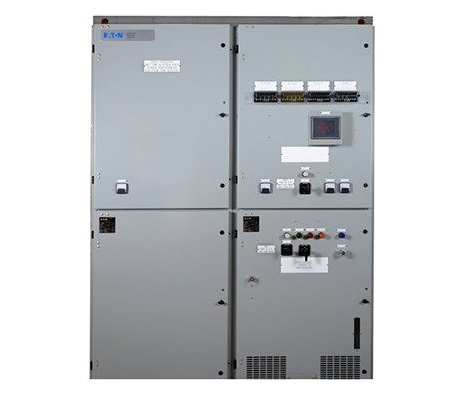

- Metal-Enclosed MV Switchgear: Compared to metal-clad switchgear, the components of metal-enclosed switchgear can be installed in common compartments and do not require mandatory partitioning.

- Pad-Mounted MV Switchgear: Designed for underground distribution systems with rated voltages from 5 to 38kV. This device has a low profile, making it suitable for line sectionalizing and circuit protection applications.

- Subsurface MV Switchgear: Designed for power distribution systems with ratings from 15 to 38kV, requiring switches and accessories that can be operated in a vault or below ground level. This device allows users to operate the switch from the ground level manually or use relays and vacuum interrupters for load protection and fault isolation.
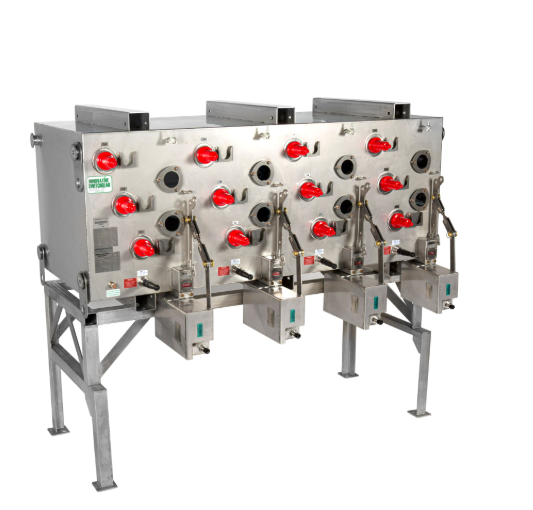
- Arc-Resistant MV Switchgear: Capable of diverting the electric arc to a containment compartment, where it is then released in an area that does not pose a hazard to operators or equipment.
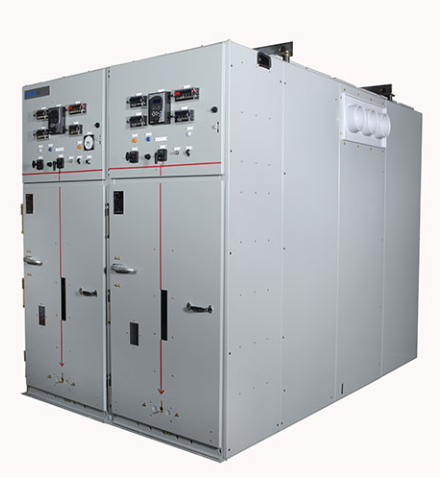

Prominent Medium Voltage Switchgear Brands
ABB Medium Voltage Switchgear
ABB MV switchgear has an operating voltage of 1kV to 52kV according to the IEC Standard, including air-insulated and gas-insulated MV switchgear. The brand's products are equipped with monitoring, diagnostic, automation, and control features, helping operators optimize inspection and handling processes.

ABB offers popular MV switchgear lines including: ABB Recloser, ABB HD4 SF6 gas, and ABB VD4 vacuum.
Siemens Medium Voltage Switchgear

The Siemens VCB MV Switchgear with code 3AF01 has a compact size, saving space, with a sealed SF6 insulation system that minimizes SF6 gas leakage, while also being moisture-proof, flame-resistant, and capable of withstanding harsh environments. This device can be installed indoors or in outdoor compact substations.
Mitsubishi Medium Voltage Switchgear

Mitsubishi offers the VF-D Series and 10-VPR-D Series Vacuum Circuit Breakers (VCB) with a vacuum valve design that provides arc control and modern insulation technology. Mitsubishi's VCB uses steel material and an entirely Chromium-free anti-corrosion technology (Chromium is harmful to the soil environment), making it completely environmentally friendly.
Frequently Asked Questions about Medium Voltage Switchgear
Question 1: How do a circuit breaker and a disconnector differ?
Answer: A circuit breaker is used for switching under load, no-load, and tripping during a fault, while a disconnector (or isolating switch) is used for switching under no-load, creating a visible safety clearance during repair and operation of the electrical system.
Question 2: What is the function of MV switchgear?
Answer: Current MV switchgear is primarily used for switching and protecting the electrical circuit against overload and short circuit faults. Additionally, this device is capable of switching capacitive current; performing ON/OFF switching or switching inductive current, etc.
Question 3: What are the common issues with MV switchgear?
Answer: MV switchgear can suffer from mechanical failures due to lack of lubrication, inadequate working environment, or component damage, leading to interruption of the tripping process. Simultaneously, this switching device can also cause partial discharge, affecting the insulation system within the equipment.


